Students need opportunities to develop knowledge, understanding and skills of the functional and the formal nature of language. In a previous post, we explored the idea of introducing young learners to experiential functions of text through the systemic functional linguistics (SFL) metalanguage of Processes, Participants, and Circumstances.
These “chunks of meaning” (Derewianka, 2011, p.55) correspond to traditional grammatical forms. For example, Participants (people, places, things) correspond to nouns, noun groups and pronouns. Processes (actions) correspond to verbs and verb groups. Surrounding Circumstances that detail the ‘when’, ‘where’ and ‘how’ correspond to adverbs and adverbial groups. In a more advanced functional analysis, we can further differentiate Participant from its description, introducing the functional category of Attributes. Attributes take the form of adjectives and adjectival groups.
There are a lot of possible written text-based teaching and learning activities around mapping functional meaning and grammatical forms, some of which will be explored in coming posts (1, 2). However, these require some sort of legend or key. The following key is proposed, indicating traditional (mostly word-based) grammar forms by typographical emphasis (bold, italic, underline). This requires text formatting which can be performed by the teacher in advance. The functional elements, which often involve multiple words in a row, can be highlighted by the students using colours. This approach allows student to focus on mapping functional elements of language. At the same time, they are provided with an opportunity to develop an understanding of the formal nature of language.
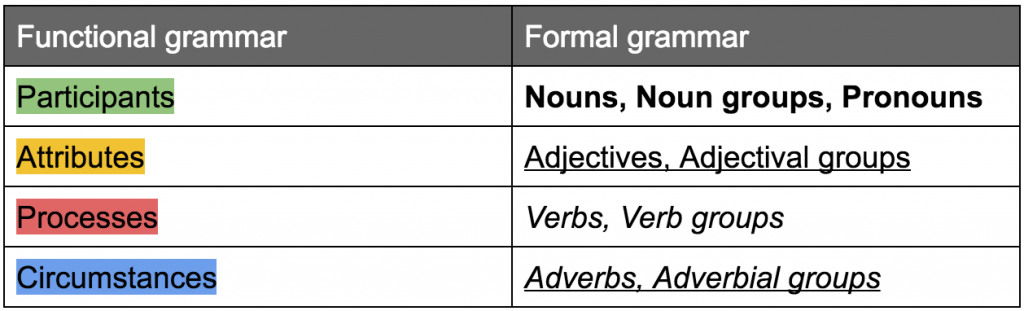
Key for working with functional and formal grammar
Applied to the opening sentences of ‘The secret garden’, this would look like:

Mapping functional meaning and grammatical forms using typographical emphasis (teacher) and highlighting (students)
The developed key is an example for the practical implementation of a continuum in approaches to describing language. As proponents of functional grammar argue, it is important not to “abandon
traditional grammar but [… to] build on it” (Derewianka & Jones, 2010, p.10).
References:
- Derewianka, B., & Jones, P. (2010). From traditional grammar to functional grammar: Bridging the divide. NALDIC Quarterly, 8 (1), 6-17.
- Derewianka, B. M. (2011). A new grammar companion for teachers. Primary English Teaching Association Australia.
- Hodgson Burnett, F. (1911). The secret garden. Project Gutenberg EBook.
Further reading:
- Exley, B., & Kervin, L. (2013). Playing with grammar in the early years: Learning about language in the Australian Curriculum: English. Australian Literacy Educators’ Association. (in particular Chapter 4, Colour coding: meanings in clauses)
Relevance to Australian Curriculum content descriptors:

